Details of the Drug
General Information of Drug (ID: DM7YCK3)
| Drug Name |
Thiabendazole
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Synonyms |
Biogard; Bioguard; Bovizole; Cropasal; Drawipas; Eprofil; Equizole; Hymush; Lombristop; Mertec; Mertect; Mintesol; Mintezol; Mintezole; Minzolum; Mycozol; Nemacin; Nemapan; Omnizole; Ormogal; Pitrizet; Polival; RPH; Sistesan; Storite; Tbdz; Tebuzate; Tecto; Testo; Thiaben; Thiabendazol; Thiabendazolum; Thiabendole; Thiabenzazole; Thiabenzole; Thibendole; Thibenzol; Thibenzole; Thiprazole; Tiabenda; Tiabendazol; Tiabendazole; Tiabendazolum; Tobaz; Tresaderm; Triasox; Tubazole; Captan T; Equivet TZ; Equizole A; Helmindrax octelmin; Hokustar HP; Mertect lsp; RTU Flowable Fungicide; Tecto B; Tecto rph; Thibenzole att; Top Form Wormer; Chemviron TK 100; G 491; MK 360; Mertect 160; Mertect 340f; Metasol TK 100; Metasol tk 10; PS1057_SUPELCO; Sanaizol 100; Syntol M100; TBZ 6; TBZ 60W; Tecto 10P; Tecto 40F; Tecto 60; Thibenzole 200; Tibimix 20; APL-luster; Arbotect (TN); MK-360; Metasol TK-100; Mintezol (TN); TBZ-6; Thiabendazole (USP); Thiabendazole [BSI:ISO]; Thiabendazole [USAN:BAN]; Tiabendazolum [INN-Latin]; Tresaderm (TN); E-Z-Ex; Mintezol, Equizole, Thiabendazole; Tiabendazol [INN-Spanish, French]; Tiabendazole (JAN/INN); 2-(1,3-Thiazol-4-yl)-1H-benzimidazole; 2-(1,3-Thiazol-4-yl)benzimidazole; 2-(1,3-thiazol-4-yl)-1H-1,3-benzodiazole; 2-(4'-Thiazolyl)benzimidazole; 2-(4-Thiazolyl)-1H-benzimidazole; 2-(4-Thiazolyl)benzimidazole; 2-(Thiazol-4-yl)benzimidazole; 2-Thiazol-4-yl-1H-benzoimidazole; 2-Thiazole-4-ylbenzimidazole; 2-[4-Thiazoly]benzimidazole; 4-(1H-benzimidazol-2-yl)-1,3-thiazole; 4-(2-Benzimidazolyl)thiazole
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Indication |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Therapeutic Class |
Antinematodal Agents
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Affected Organisms |
Roundworms, hookworms, and other helminth species
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ATC Code |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Drug Type |
Small molecular drug
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Structure |
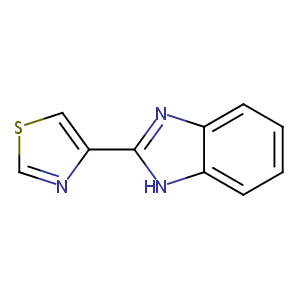 |
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| 3D MOL | 2D MOL | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| #Ro5 Violations (Lipinski): 0 | Molecular Weight (mw) | 201.25 | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Logarithm of the Partition Coefficient (xlogp) | 2.5 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Rotatable Bond Count (rotbonds) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Donor Count (hbonddonor) | 1 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Hydrogen Bond Acceptor Count (hbondacc) | 3 | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| ADMET Property |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Chemical Identifiers |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Cross-matching ID | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Repurposed Drugs (RPD) | Click to Jump to the Detailed RPD Information of This Drug | |||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Molecular Interaction Atlas of This Drug
 Drug Therapeutic Target (DTT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
 Drug-Metabolizing Enzyme (DME) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
 Drug Off-Target (DOT) |
|
|||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
| Molecular Interaction Atlas (MIA) | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
Drug-Drug Interaction (DDI) Information of This Drug
|
Coadministration of a Drug Treating the Disease Different from Thiabendazole (Comorbidity)
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
References
